The Sun has now entered its “solar maximum period” in the current solar cycle, resulting in a noticeable increase in sunspots and heightened solar activity. Jamie Favors, the head of NASA’s Space Weather Program, explains that the solar maximum is a phase characterised by a significant rise in sunspots and solar phenomena, which can have real-world implications for life on Earth.
Favours highlights the dual nature of this increased solar activity, stating, “This surge provides an exciting opportunity to learn about our closest star — but it also leads to tangible effects on Earth and throughout our solar system.” The solar maximum period presents both exciting opportunities for scientific exploration of solar phenomena and potential challenges for technological systems on Earth. As researchers continue to monitor solar activity, they remain vigilant for its implications on life and technology in our increasingly interconnected world.
NASA and NOAA announce the sun’s transition to solar maximum
During a teleconference on Tuesday, October 15, 2024, representatives from NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the Solar Cycle Prediction Panel announced that the Sun has officially entered its solar maximum period. The solar cycle represents the natural fluctuation of the Sun as it moves between periods of low and high activity. Approximately every 11 years, at the peak of this cycle, the Sun’s magnetic poles flip—similar to the North and South Poles on Earth swapping positions every decade—marking a transition from a quieter phase to a more active and turbulent one.
In the solar maximum phase, the Sun is capable of producing massive explosions of light, energy, and solar radiation, resulting in conditions referred to as space weather. This space weather can have significant effects on satellites and astronauts in space, as well as disrupt communication systems—such as radio and GPS—and power grids on Earth. When solar activity is at its peak, space weather events become more common. Recent solar events, like the storm in May 2024, have contributed to heightened aurora visibility and impacted satellites and infrastructure over the past few months.
What is solar maximum?
Solar maximum is a crucial phase within the Sun’s 11-year solar cycle, during which the Sun undergoes fluctuations in its magnetic activity. This cycle often culminates in a solar maximum, a point at which solar activity intensifies. Interestingly, this period is associated with the potential reversal of the Earth’s magnetic North and South poles, a phenomenon that can occur approximately every decade due to the Sun’s magnetic field dynamics.

Image source: NASA
As the Sun reaches its solar maximum, the surface becomes populated with an increased number of sunspots and experiences a greater frequency of solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). Sunspots are dark regions on the Sun’s surface that are cooler than their surrounding areas and serve as the epicentres of solar eruptions.
Effects of solar maximum on Earth
The solar flares and CMEs emitted during the solar maximum lead to solar storms that inundate Earth with charged particles. When these solar emissions reach our planet, they interact with Earth’s magnetic field, resulting in geomagnetic storms. These storms can disrupt satellite communications and interfere with radio and GPS signals, and in severe cases, they may even affect power grid operations.
Future solar activity remains uncertain despite current solar maximum announcement
Despite the announcement of the solar maximum period, Elsayed Talaat, the director of space weather operations at the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC), cautions that this does not signify the peak of solar activity for the current cycle. “While the Sun has reached the solar maximum period, the month in which solar activity peaks will not be determined for several months or even years,” she noted.
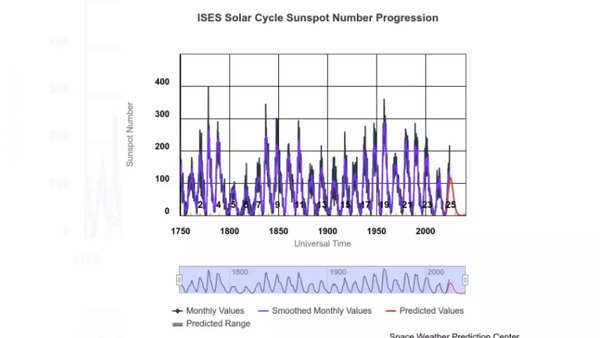
Image Source: NASA
Additionally, Lisa Upton, lead scientist at the Southwest Research Institute and co-chair of the Solar Cycle Prediction Panel, remarked that sunspot activity during Solar Cycle 25 has slightly surpassed expectations. However, she pointed out that while a few significant storms have occurred, they do not exceed the typical intensity expected during the maximum phase of the solar cycle.
Also Read | James Webb Space Telescope captures groundbreaking image of AF Leporis b, the lowest-mass exoplanet ever observed