NEW DELHI: Nearly 28% of grains supplied by Food Corporation of India (FCI) and state governments never reach the intended beneficiaries and the economic loss to the exchequer is estimated to be more than Rs 69,000 crore, a paper by an economic think tank has revealed and called for urgent reforms of the system.
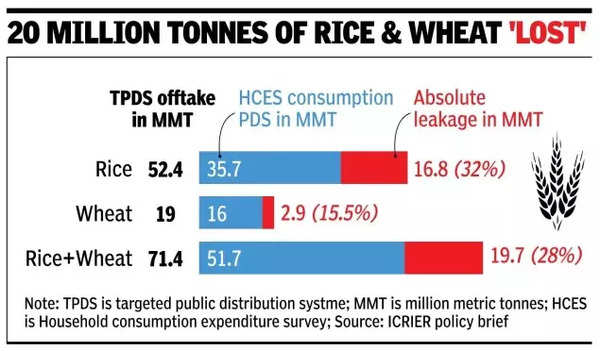
Analysing data from the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) and FCI’s monthly offtake numbers from August 2022 to July 2023, the paper estimates that 20 million tonnes of rice and wheat fail to reach their intended beneficiaries.
“This is an annual loss. Where is it going? Maybe it is being diverted to the open market or for even exports,” said Ashok Gulati, Infosys chair professor at ICRIER, who authored the policy brief with Raya Das and Ranjana Roy.
The paper said this leakage of 20 million tonnes of rice and wheat translates into a substantial financial burden, costing the exchequer Rs 69,108 crore, considering the economic cost of wheat and rice for that year.
“While this figure represents a significant improvement from the 46% leakage reported in 2011-12, it still indicates that a substantial portion of the free/subsidised grains is not reaching the intended beneficiaries,” the paper said, referring to the 2015 report of a govt-appointed panel which was put in the backburner. It also said that the introduction of point of sale (POS) machines in fair price shops (ration shops) in 2016 has helped in plugging some of the gap but leakage is still substantial.
It says, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland in the North-East, followed by Gujarat, are the top three states in terms of PDS leakage.
Lack of digitalisation in the northeastern states have been identified as one of the major reasons for the higher leakage.
The paper said that Bihar and West Bengal have achieved significant reductions in PDS leakage over the past decade. In Bihar, it dropped sharply from 68.7% in 2011-12 to just 19.2% in 2022-23. West Bengal saw a decrease from 69.4% to 9%.
In UP, PDS leakage is estimated at 33%, with the state topping the list in terms of the absolute quantity of grains leaked, according to the paper. Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Maharashtra experience high rates of siphoning, which often involves grains being diverted back to the open market, the paper adds.
The paper states that linking the ration card of beneficiaries with Aadhaar for PDS has increased the efficacy of distribution, but leakage in PDS still remains a concern.
“Despite the implementation of digital tracking systems, leakage persists, highlighting the need for not only improved monitoring but also structural reforms to address PDS corruption,” according to the paper.
It has suggested key reforms of the PDS system which include improving the accuracy of beneficiary targeting and exploring a transitioning to food stamps or voucher system and direct cash transfer, “which could enhance transparency, reduce inefficiencies, and ensure nutrition security”.
India operates one of the largest PDS in the world providing free gains which includes rice and wheat to about 814 million people.